
Initial settings would include P high at the P plat, desired P mean + 3 cm H 2O, or previous mean airway pressure, with a maximum of less than 35 cm H 2O T high at 4.5 to 6 seconds with respiratory rate of 8 to 12 beats/min P low at 0 cm H 2O and T low at 0.5 to 0.8 seconds with a target tidal volume of 4 to 6 mL/kg.

#Pip in mechanical ventilation full#
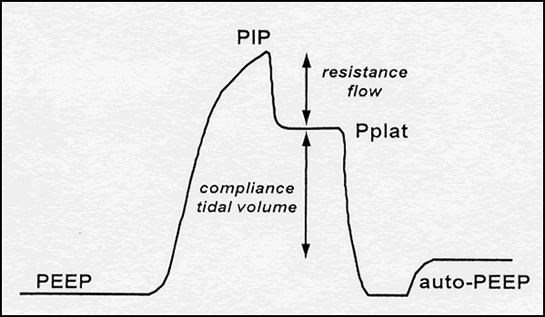
There is less chance of overdistension given not “filling” lung but “emptying.” The short release time does not allow significant derecruitment. Pressure Control Ventilation (ACPC, PCV, CMV-PC) is a full control mode of ventilationthe ventilator will control all phases of the breath delivered based on the set parameters. The pressure release feature allows for improved tidal volume (V T) for given ΔP by utilizing increased elastic recoil. PIP: Total inspiratory work by vent Reflects resistance & compliance Normal 20 cmH20 (8cc/kg and adult ETT) Resp failure 30-40 (low VT use) Concern if >. The increased time at high pressures may improve recruitment. 38 Advantages include improved oxygenation and compliance secondary to spontaneous breathing, which improves V̇/Q̇ matching, increased cardiac output from improved venous return due to decreased intrathoracic pressure and right atrial pressure, improved perfusion to gastrointestinal tract and glomerular filtration rate, and decreased sedation and neuromuscular blockade use. In seven patients, the diagnosis or estimation of severity of pulmonary infiltrates would have been altered if only the film during PEEP had been available.

It is essentially the sum of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and time-cycled pressure release. This modified bilevel mode allows spontaneous breathing to occur at the upper pressure level (IRV), which is usually maintained throughout a long inspiratory phase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
